In the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), attributes and metadata represent much more than simple supplementary information: they constitute the intelligent backbone of digital models. These structured data, invisible but essential, can represent up to 70% of the total value of a CAD model according to industry experts. At a time when interoperability and digital continuity are becoming strategic issues, mastering these attributes radically transforms the productivity of industrial companies.
Discover how modern visualization solutions now allow full exploitation of this essential technical data, accelerating development processes and optimizing collaboration among all stakeholders in the value chain.
Table of Contents
- The Fundamentals of CAD Attributes and Metadata
- Strategic Issues for Industrial Companies
- Technical Challenges and Common Obstacles
- 3DViewStation: Complete Solution for Attribute Management
- Use Cases and Practical Applications
- Best Practices for Attribute Optimization
- Future Trends and Evolution Perspectives
The Fundamentals of CAD Attributes and Metadata
Attributes in computer-aided design constitute all non-geometric information associated with 3D models. This technical data considerably enriches the value of digital representations by providing context, specifications, and intelligence to modeled components.
Definition and Typology of Attributes
CAD metadata is divided into several fundamental categories:
- Identification attributes: references, designations, serial numbers, nomenclatures
- Technical attributes: materials, tolerances, surface treatments, physical properties
- Functional attributes: component role, interfaces, assembly constraints
- Management attributes: versions, validation states, authors, modification dates
- Manufacturing attributes: processes, suppliers, associated costs
This information, though invisible in the classic three-dimensional representation, constitutes critical data for the effective exploitation of digital models throughout the product lifecycle.
Attribute Formats and Standards
The diversity of CAD systems has generated multiple formats for storing and exchanging attributes. While some standards like STEP AP242 or JT contribute to harmonization, the industrial reality remains marked by significant heterogeneity in metadata structuring.
| Format | Attribute Management | Interoperability |
|---|---|---|
| Native formats (CATIA, NX, Creo...) | Complete but proprietary | Limited to tools from the same vendor |
| STEP AP242 | Standardized but sometimes incomplete | High but possible losses |
| JT | Good management of PMI/attributes | Strong in the industrial ecosystem |
| 3D PDF | Limited but customizable support | Excellent for document sharing |
Preserving attributes during conversions between formats constitutes a major challenge for maintaining the integrity and value of digital models.
Strategic Issues for Industrial Companies
Digital Continuity and Value Chain
Mastering CAD attributes represents a strategic lever for ensuring digital continuity within industrial organizations. Effective management allows:
- Elimination of manual re-entry between systems (error reduction up to 90%)
- Acceleration of product development processes (time reduction of 30% to 50%)
- Improvement of documentation quality through information consistency
- Optimization of decision-making processes thanks to reliable and accessible data
In a context where industrial products are becoming increasingly complex, the richness of attributes associated with digital models becomes a determining factor of competitiveness.
Intellectual Property Protection
CAD attributes represent a substantial part of companies' intellectual property. Their management necessarily involves consideration of:
- Selective filtering of sensitive metadata during external exchanges
- Controlled alienation of geometries for secure sharing
- Traceability of access to strategic technical information
- Prevention of sectioning operations on shared models
These protection mechanisms constitute a delicate balance between necessary sharing and strategic confidentiality of technical data.
Technical Challenges and Common Obstacles
Despite their crucial importance, CAD attribute management presents several technical challenges that still limit their optimal exploitation.
Fragmentation and Heterogeneity
The multi-CAD environment that characterizes most industrial organizations generates problematic fragmentation of metadata:
- Diversity of attribute structures according to CAD systems
- Loss of information during conversions between formats
- Duplication of data across different information systems
- Absence of a unique reference for nomenclatures and conventions
This fragmentation constitutes a major obstacle to the cross-functional exploitation of technical data and interoperability between departments.
Performance and Volume
Complex assemblies, sometimes consisting of tens of thousands of components, generate a considerable amount of metadata. This volume poses significant challenges:
- Prohibitive loading times for large assemblies
- Difficulties in indexing and searching attributes
- Limitations of real-time filtering capabilities
- Degraded performance during mass attribute modifications
In this context, traditional CAD solutions often reach their limits, compromising user experience and slowing down industrial processes.
3DViewStation: Complete Solution for Attribute Management
3DViewStation distinguishes itself as a powerful and intuitive solution for exploiting attributes and metadata in CAD models. Its pragmatic approach addresses the main challenges faced by manufacturers.
Import Capabilities and Attribute Preservation
One of 3DViewStation's major strengths lies in its ability to natively import CAD attributes from a wide range of formats:
- Native support for major CAD formats (CATIA, NX, Creo, SolidWorks, etc.)
- Complete preservation of attributes during conversions
- Fast import of large assemblies (5 GB or 20,000 parts in seconds)
- Selective loading of attributes to optimize performance
This reliable import capability ensures essential digital continuity in industrial processes.
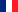
Intelligent Visualization and Navigation
3DViewStation offers a modern and intuitive interface to efficiently explore attributes associated with CAD models:
- High-performance DirectX interface requiring little or no training
- Contextual visualization of attributes when hovering over components
- Hierarchical organization of information for smooth navigation
- Dynamic filtering of components based on their attributes
- Automatic generation of bills of materials (BOM) from metadata
This visual approach considerably facilitates access to technical information, even for occasional users.
Attribute Enrichment and Creation
Beyond simple visualization, 3DViewStation offers advanced features to enrich CAD models:
- Addition of custom attributes via an intuitive graphical interface
- Import of attributes from external sources (CSV, Excel, etc.)
- Creation of derived attributes based on geometric analyses
- Association of annotations and markings with components
- Creation of hyperlinks to technical documentation
This enrichment capability transforms 3DViewStation into a collaborative platform for documenting and exploiting digital models.
Attribute-Based Analysis
The analytical features of 3DViewStation fully exploit attributes to offer unprecedented perspectives:
- Model comparison with analysis of attribute modifications
- Interference detection enriched by technical metadata
- Wall thickness analysis contextualized by materials
- Automatic recognition of features (holes, tubes, etc.)
- Dimensional measurements associated with functional specifications
These analytical capabilities allow exploiting the richness of attributes for a deeper understanding of digital models.
Intellectual Property Protection
3DViewStation integrates advanced mechanisms for protecting sensitive data:
- Controlled alienation of geometries for secure sharing
- Selective filtering of visible attributes according to recipients
- Prevention of sectioning operations on shared models
- Automatic removal of non-visible internal components
These features allow controlled sharing of CAD models without compromising the company's intellectual property.
Use Cases and Practical Applications
The advanced attribute management capabilities offered by 3DViewStation materialize through numerous industrial use cases.
Enhanced Technical Documentation
Intelligent exploitation of attributes allows generating a new generation of technical documentation:
- Automated creation of structured bills of materials directly from the model
- Generation of interactive callouts associating components and specifications
- Production of multilingual technical documentation based on attributes
- Enrichment of the model with links to external resources
This approach considerably reduces documentation creation time while improving the consistency and accuracy of technical information.
Collaborative Design Reviews
Attributes play a central role in design review processes:
- Rapid identification of critical components via their attributes
- Contextual filtering to focus attention on specific issues
- Collaborative annotations progressively enriching the model
- Tracking of attribute changes between different versions
These features transform design reviews into truly collaborative and effective processes.
Integration with Information Systems
3DViewStation naturally integrates into the company's information ecosystem:
- Bidirectional synchronization with PLM systems (Teamcenter, 3DEXPERIENCE, etc.)
- Feeding ERP systems with technical attributes
- Connection with document management platforms
- Interface with product configurators and technical catalogs
This interoperability ensures the consistency of technical information across all company information systems.
Best Practices for Attribute Optimization
Optimal exploitation of CAD attributes relies on several fundamental best practices.
Standardization and Governance
A structured approach to attributes constitutes an essential prerequisite:
- Definition of a standardized attribute repository for the organization
- Establishment of consistent naming conventions
- Implementation of validation processes for critical attributes
- Team training on best practices for metadata management
This standardization considerably facilitates cross-functional exploitation of technical information and ensures its consistency over time.
Progressive Enrichment Strategy
The enrichment of CAD models must be part of a progressive and targeted approach:
- Identification of high value-added attributes according to business processes
- Prioritization of enrichment efforts according to expected gains
- Automation of recurring enrichment processes
- Regular validation of attribute quality and relevance
This pragmatic approach optimizes the return on investment of efforts devoted to enriching digital models.
Multi-Contextual Exploitation
The true value of attributes lies in their adapted exploitation in different business contexts:
- Definition of specific business views filtering relevant attributes
- Adaptation of interfaces according to the needs of different functions
- Customization of reports and nomenclatures according to usage
- Targeted user training for attribute exploitation in their context
This contextual exploitation maximizes the value of metadata by making it directly actionable by each business function.
Future Trends and Evolution Perspectives
CAD attribute management is evolving rapidly, driven by several major technological trends.
Artificial Intelligence and Automated Enrichment
AI technologies are progressively transforming attribute management:
- Automatic recognition of features and attribute generation
- Contextual suggestions based on data history
- Detection of inconsistencies and anomalies in attributes
- Predictive enrichment according to anticipated uses
These technologies pave the way for a new generation of "self-documented" and intelligent digital models.
Enhanced Digital Twins
The evolution towards complete digital twins relies heavily on advanced attributes:
- Integration of behavioral data alongside static attributes
- Synchronization with data from the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Temporal historization of evolving attributes
- Simulation and prediction based on dynamic attributes
This convergence between physical and digital worlds fundamentally relies on the richness and quality of attributes associated with models.
Augmented Reality and Contextual Visualization
The emergence of augmented reality (AR) technologies opens new perspectives for attribute exploitation:
- Contextual visualization of attributes superimposed on the real world
- Instant access to technical information in the field
- Immersive training exploiting pedagogical attributes
- Assisted maintenance guided by technical attributes
These technologies radically transform the accessibility and actionability of technical information contained in CAD attributes.
In conclusion, CAD attributes and metadata now represent a major strategic issue for industrial organizations. Their effective management through solutions like 3DViewStation constitutes a determining performance lever in a context of digital transformation. From design to maintenance, through manufacturing and documentation, CAD attributes considerably enrich the value of digital models and pave the way for more agile, collaborative, and innovative industrial processes.